This post is the first of two by Executive Director Roberts on the FAO’s constitutional framework.
The Resnick Center is honored to be a partner to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The FAO was established in 1945 when its Constitution was signed and ratified by nations meeting in Quebec, Canada. It was created as part of U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s broader efforts to advance the “Freedom from Want,” an aspiration he articulated in response to the catastrophic human suffering caused by hunger and malnutrition. The vision of an international organization grounded in governance principles was also central to the post-World War II global reordering.
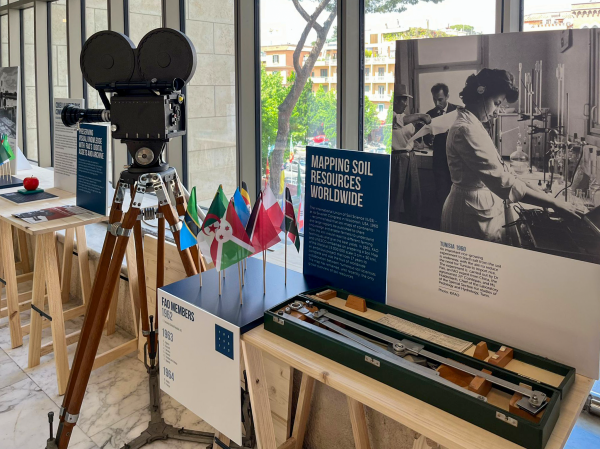
In May, I was honored to attend the next phase of a Constitution Exhibition in Rome – a project that I helped create that celebrates and contextualizes the role of the FAO Constitution in shaping the organization’s operations and aspirations. The exhibition complements my ongoing research and writing on the development of FAO’s constitutional framework from 1943 to 1945, as well as its further development and subsequent application in global food governance through 1965.
Continue reading “Executive Director Roberts on Partnering with the FAO on its Constitution Exhibition”








You must be logged in to post a comment.